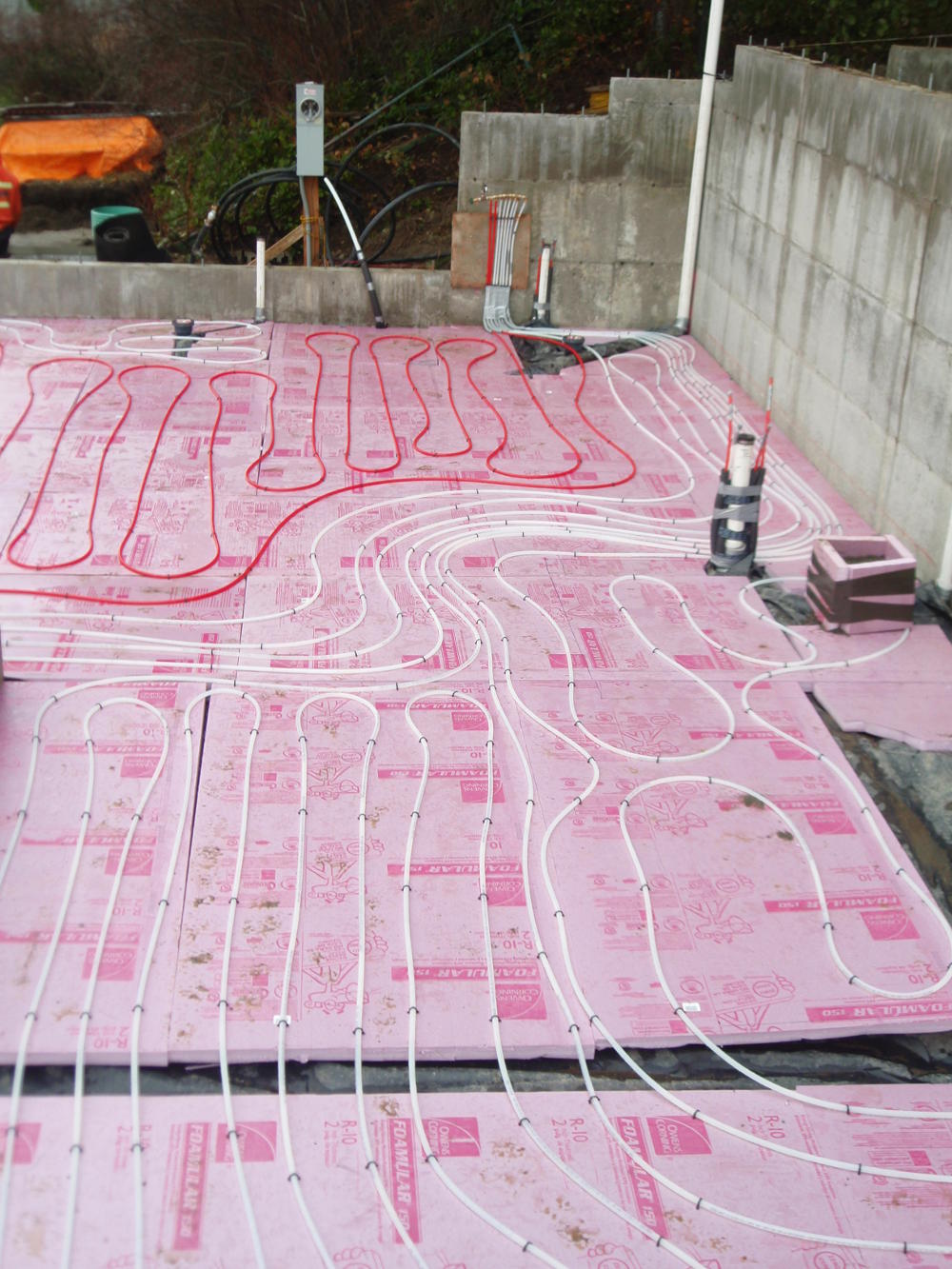
Radiant Floor Heating: In a radiant floor heating system, warm water flows through flexible plastic tubing called PEX that is located underneath or within the floors. The PEX tubing carries the warm water into specific rooms or “zones” to effectively heat people and objects in every corner of the room.Radiant Floor Heating: In a radiant floor heating system, warm water flows through flexible plastic tubing called PEX that is located underneath or within the floors. The PEX tubing carries the warm water into specific rooms or “zones” to effectively heat people and objects in every corner of the room.
Radiant Floor Heating: In a radiant floor heating system, warm water flows through flexible plastic tubing called PEX that is located underneath or within the floors. The PEX tubing carries the warm water into specific rooms or “zones” to effectively heat people and objects in every corner of the room.Radiant Floor Heating: In a radiant floor heating system, warm water flows through flexible plastic tubing called PEX that is located underneath or within the floors. The PEX tubing carries the warm water into specific rooms or “zones” to effectively heat people and objects in every corner of the room.
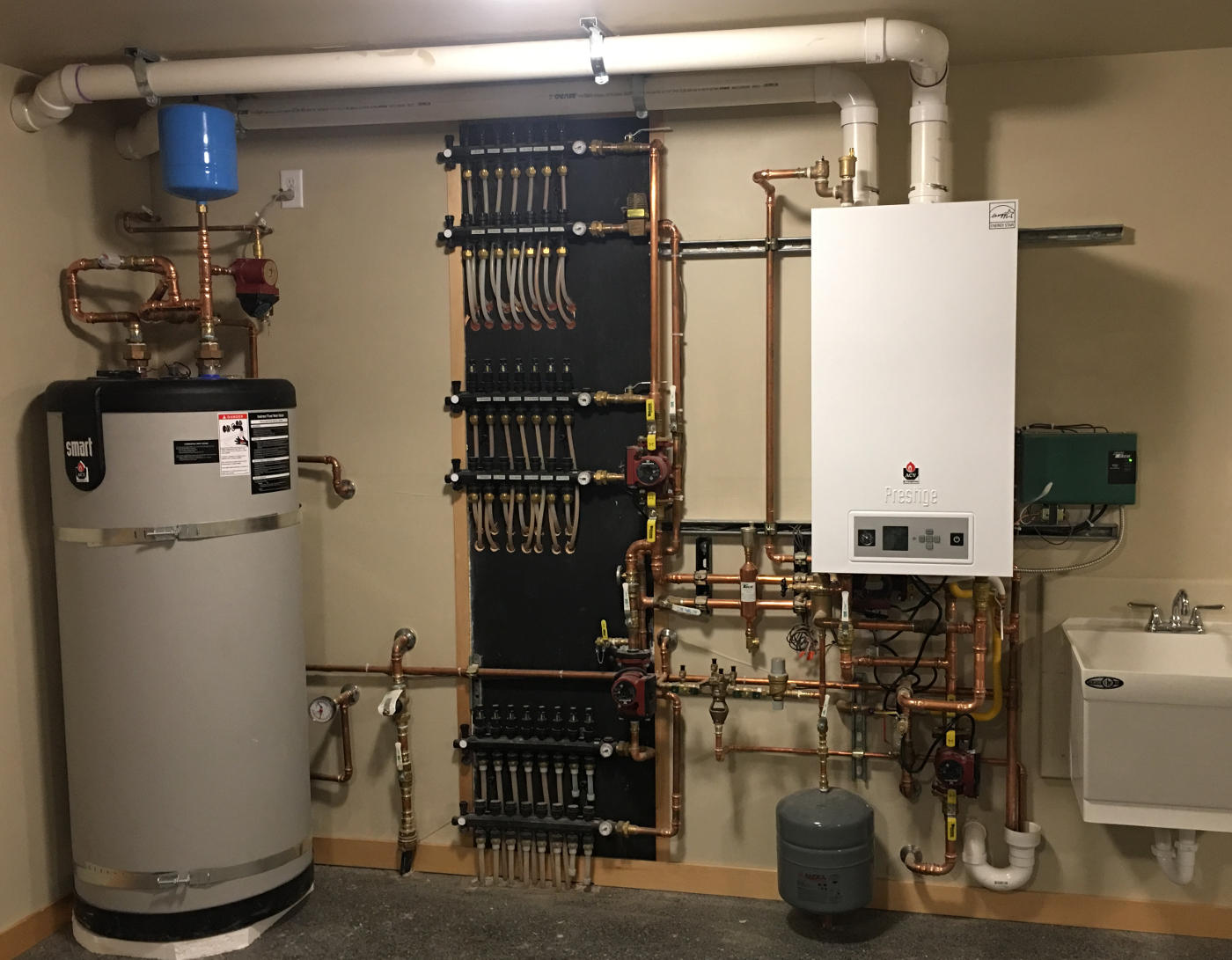
In addition to the PEX tubing, the other main components in a radiant heating system include a heat source, pumps, manifolds and controls. The heat source in a hydronic radiant floor heating system is typically a boiler or a hot-water heater. However, other heat sources can be used, including highly energy-efficient sources such as geothermal and solar.
Because a radiant floor heating system is designed in zones, you have the luxury of changing temperatures for each room, depending on its use. This makes the system even more energy efficient because unoccupied or lower-use rooms (such as a guest bedroom or formal dining room) can be set to a lower temperature than rooms with greater use (like a kitchen, bathroom or basement).
Radiant vs. Forced Air: The water in a radiant system has a capacity to transport energy 3,500 times greater than air, so it can heat (and even cool) using less energy than a forced-air system. This amounts to greater comfort at a lower thermostat setting, which provides lower energy bills. In fact, more people are comfortable with radiant floor heating at a lower thermostat setting than with forced-air heating at a higher thermostat setting.
Hot Water Baseboard System: Similar to radiant heat, this system uses hot water heated by a boiler to heat a space by a combination of radiation and convection. Hot water heated by boiler and piped to "fin-tube" baseboard units mounted along walls. The fins increase the surface area of heat dissipation making the unit more efficient. Air is distributed by convection as air rises and is heated by the baseboard unit. The boiler may be fueled by natural gas, propane, oil or electricity. Baseboard radiation / convection units must remain unobstructed and can provide challenges in furniture placement and drape design.